7 Oldest Archaeological Sites in China
Table of Contents
- 1. Renzidong Relic Site
- 2. Jianshi Upright Man Site
- 3. Shangchen Site
- 4. Longgupo Site
- 5. Xihoudu Site
- 6. Yuanmou Man Site
- 7. Nihewan Site Group
Prehistory is the vast period of time where no written records documented human activity exist. Traditionally, archaeologists divide the prehistoric period into three archaeological periods: the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age. The Stone Age is subdivided into the Palaeolithic (or Old Stone Age), Mesolithic (or Middle Stone Age), and Neolithic (or New Stone Age).At present, over 2,000 Paleolithic sites have been discovered in China, covering various periods from 2.59 million to 10,000 years ago.
The Chinese archaeological sites on this list, including the famous Yuanmou Man Site, are the oldest ancient archaeological sites in China by now. These archaeological discoveries in China are of great importance in studying early humans.
Renzidong Relic Site
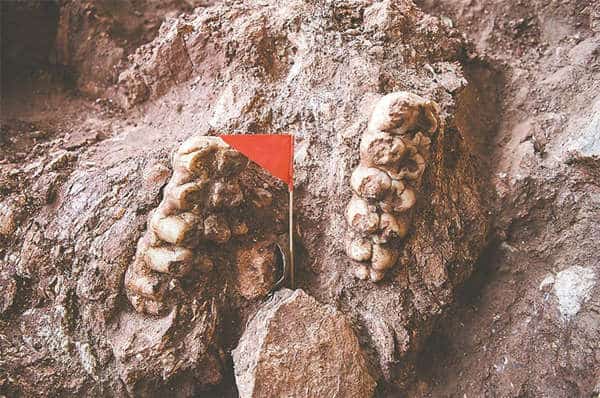
The archaeological site of Renzidong or Renzi Cave is a Paleolithic site. It’s located in present-day Suncun Town, Fanchang District, Wuhu City, about 170 km from the famed HuangshanYellow Mountain. Fanchang Renzidong Site is the oldest site showing early hominins in Asia. Its fauna is relatively ancient in the Quaternary fauna, and its geological age is the Early Pleistocene.
Evidence of Renzidong was first discovered in 1984 as workers were quarrying limestone. But excavation of the fossil site of Renzidong didn’t begin until 1998. Archaeological excavations uncovered animal bones and possible stone tools that suggest ancient human activities over two million years ago. The discovery made Renzidong ruins one of the earliest known sites of ancient human activities in Eurasia.
Jianshi Upright Man Site
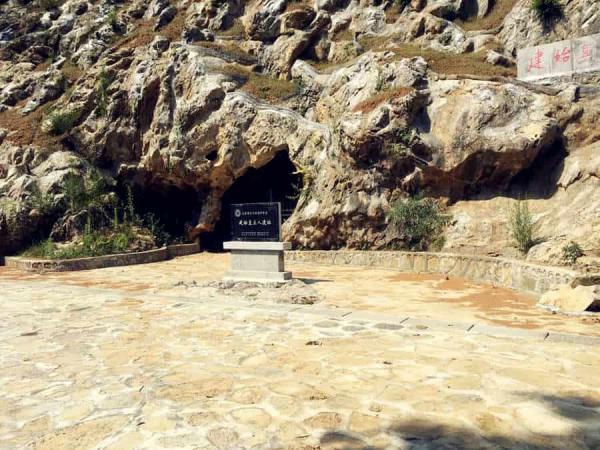

Jianshi Man Site, also known as Juyuandong (巨猿洞) or Longgudong (龙骨洞), is situated in Gaoping Town, Jianshi County, over 450 km away from Wuhan City and around 160-170 km to Yichang Yangtze River Cruise ports. Though not a well-known archaeological site in China, the Jianshi site is one of the earliest ancient human sites discovered in China.
The first round of excavations at the Jianshi Man Site started in 1970, followed by several successive excavations. Researchers have discovered Homo erectus teeth, stone tools, stone products, bone products, as well as associated large mammals and more than 50 small mammals. It is the first discovered fossil site where Homo erectus and giant apes coexisted.
Shangchen Site
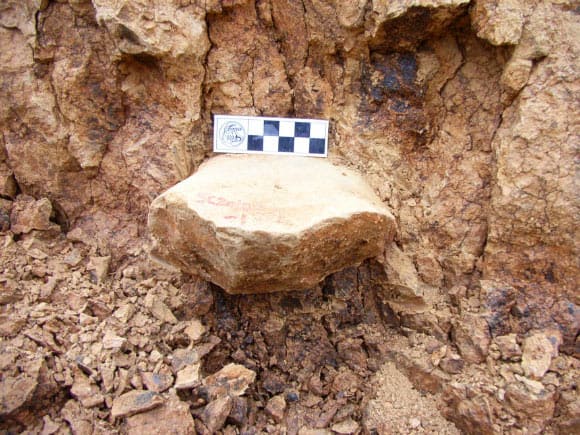

The archaeological site of Shangchen is a Palaeolithic site. It's located in Shangchen Village, Yushan Town, Lantian County, about 70 km from the famous Terracotta Army of Xi’an. Since 2004, Shangchen historical site has been carefully studied.
The fossil site of Shangchen in the southern Loess Plateau contains 17 artifact layers. Nearly 100 stone tools have been uncovered at the Shangchen site. Some of them are estimated to be 2.1 million years old. They are currently the oldest stone tools found outside Africa. These ancient chipped stone fossils are evidence of the earliest appearance of hominins outside Africa, far earlier than previously believed.
Longgupo Site
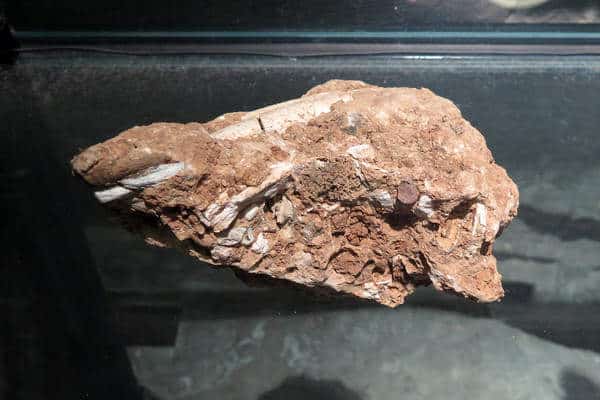

Longgupo Site, also known as Longgupo Cave, or Wushan Hominin Site (巫山猿人遗址), is a Pleistocene site situated in Longgupo (literally "Dragon Bone Slope"), Zhenlongping Village, Miaoyu Town, Wushan County. It’s over 400 km from downtown Chongqing and approximately 20 km from the south of the mighty Yangtze River.
The most astounding thing of Longgupo Cave excavation is the discovery of a fossilized fragment of mandible with two teeth and an upper incisor in 1985 which can be dated to about 2 million years ago. These human fossils were considered to represent a new subspecies of Homo erestus called Homo erectus wushanensis (Wushan Man). The discovery indicates that hominids reached Asia much earlier than thought.
Xihoudu Site

The prehistoric site of Xihoudu is located in Xihoudu Village, Ruicheng County of southern Shanxi Province, about 400 km away from Pingyao Ancient Town. Xihoudu archaeological site was first found in 1959, and subsequently started excavation in 1961.
Archaeologists unearthed many ancient cultural relics and animal fossils at Xihoudu Site, including stone artifacts, antlers with cutting marks, and burned animal bones. These ancient ruins are considered the earliest evidence of fire used by human ancestors about 1.8 million years ago.
Yuanmou Man Site
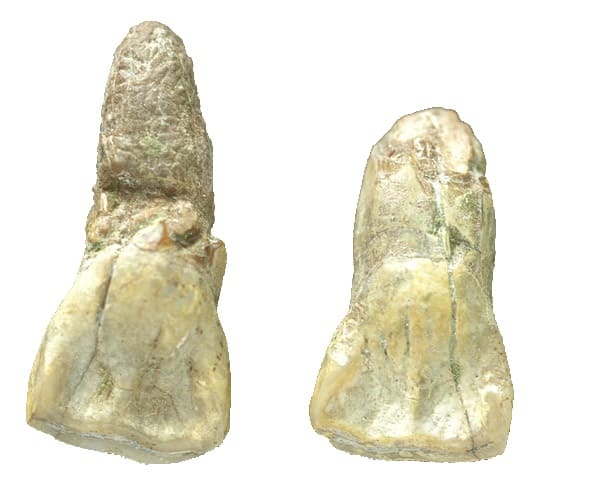

The archaeological site of Yuanmou Man is located in north of Danawu Village, Yuanmou County of Autonomous Prefecture, around 40 km from Yuanmou Wuhao Earth Forest and 180 km from Dianchi Lake of Kunming.
Two ancient human upper first incisors were found at Yuanmou Man Site in 1965. These human fossils assigned to represent a new subspecies of Homo erestus called Homo erectus yuanmouensis (Yuanmou Man). Yuanmou man fossil is one of the earliest human fossils found in China. Later, the site unearthed stool tones, charcoal remnants, and early Pleistocene animal fossils including horse, stegodon, and deer.
Nihewan Site Group
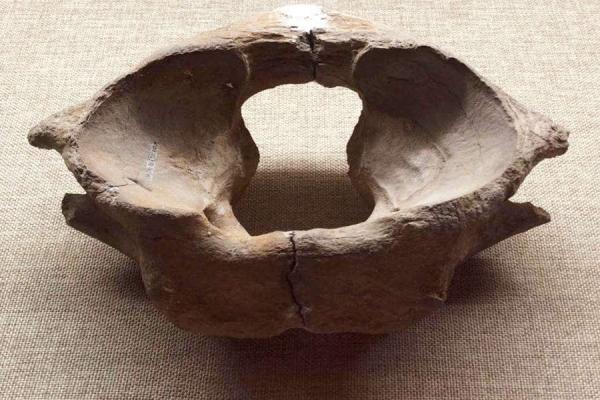

Nihewan Site generally refers to a group of archaeological sites of Nihewan, including Majuangou Site, Xiaochangliang Site, Banshan Site, Houjiayao Site, Hutouliang Site, etc. The archaeological site group is located in the east of Yangyuan County, about 160 km from the Badaling Great Wall and 190 km from Ming Tombs of Beijing.
By far, more than 80 sites of early humans have been discovered at the Nihewan ruins cluster, with 18 sites dating to over one million years. Nowhere else in the world has such a concentration of ancient human remains and a complete Paleolithic cultural sequence.


